Crypto
Crypto¶
todo http://www.wuy4n.com/2025/11/29/ZJUCTF2025wp/
Crypto-it¶
给了私钥的 RSA,会读就行:
from Crypto.PublicKey import RSA
from Crypto.Cipher import PKCS1_OAEP
with open("private_key.pem", "rb") as f:
key_data = f.read()
key = RSA.import_key(key_data)
print("[+] n =", key.n)
print("[+] e =", key.e)
print("[+] d =", key.d)
with open("flag.enc", "rb") as f:
ciphertext = f.read()
cipher_rsa = PKCS1_OAEP.new(key)
try:
plaintext = cipher_rsa.decrypt(ciphertext)
print("[+] Decrypted plaintext:")
print(plaintext)
except ValueError as e:
print("[-] 解密失败:", e)
random¶
在 _randomemodule.c 中可以发现,PRNG 在初始化时会将种子取绝对值:
static int
random_seed(RandomObject *self, PyObject *arg)
{
// ...
/* This algorithm relies on the number being unsigned.
* So: if the arg is a PyLong, use its absolute value.
* Otherwise use its hash value, cast to unsigned.
*/
if (PyLong_CheckExact(arg)) {
n = PyNumber_Absolute(arg); // 关键:取绝对值
} else if (PyLong_Check(arg)) {
_randomstate *state = _randomstate_type(Py_TYPE(self));
n = PyObject_CallOneArg(state->Long___abs__, arg); // 同样
}
// ...
}
也即是说,x 与 -x 做种子,得到的 otp 相同,加密同一个 msg 得到的密文当然也相同;结合大端序编码 key = int.from_bytes(flag.encode(), 'big'),应该从右侧开始攻击,err 逐位尝试 0/1 并获得两个密文;如果相同,说明 key 的这一位为 0;否则为 1:
from pwn import *
import sys
def query_oracle(r, err):
msg = b'\x00' * 64
r.sendafter(b'input msg: ', msg.hex().encode())
r.sendafter(b'input err: ', str(err).encode())
r.recvuntil(b'encrypted: ')
response_hex = r.recvline().strip().decode()
return bytes.fromhex(response_hex)
context.log_level = 'info'
r = remote("127.0.0.1", 2265)
recovered_int = 0
MAX_BITS = 512
for bit_idx in range(MAX_BITS):
perturbation = 1 << bit_idx
err_plus = recovered_int + perturbation
err_minus = recovered_int - perturbation
ct1 = query_oracle(r, err_plus)
ct2 = query_oracle(r, err_minus)
if ct1 is None or ct2 is None:
print("Failed to get ciphertext.")
break
if ct1 != ct2:
recovered_int |= perturbation
if (bit_idx + 1) % 8 == 0:
try:
byte_len = (recovered_int.bit_length() + 7) // 8
current_bytes = recovered_int.to_bytes(byte_len, 'big')
if b'ZJUCTF{' in current_bytes:
print(f"\nRecovering: {current_bytes}")
if current_bytes.endswith(b'}'):
print(f"Flag found: {current_bytes.decode()}")
break
except Exception as e:
print(e)
if bit_idx % 16 == 0:
sys.stdout.write(f"\r[*] Progress: {bit_idx}/{MAX_BITS} bits recovered")
sys.stdout.flush()
r.close()
print(f"\nRecovered Key: {recovered_int}")
byte_len = (recovered_int.bit_length() + 7) // 8
print(f"Flag: {recovered_int.to_bytes(byte_len, 'big')}")
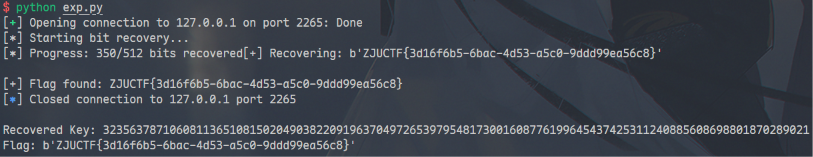
ZJUCTF{3d16f6b5-6bac-4d53-a5c0-9ddd99ea56c8}
paillier¶
服务端提供四种字符串处理方式,核心判定是:如果 actions[action](long_to_bytes(paillier.decrypt(x))) == long_to_bytes(paillier.decrypt(y)),则通过。
- 考虑同态性质:Paillier 支持加法和数乘同态
- \(E(m_1) \cdot E(m_2) \equiv E(m_1 + m_2)\)
- \(E(m)^k \equiv E(k m)\)
- 爆破 FLAG 长度:利用 "CTRL-C + CTRL-V" 处理方式,构造密文使得处理后长度为 L,遍历 L 直到判定通过
- 逐字节爆破 FLAG:每次猜测一个前缀,构造密文使得去掉前缀后长度为剩余长度,判定通过则该字节正确
from pwn import *
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes, bytes_to_long
conn = remote("127.0.0.1", 9993)
conn.recvuntil(b"n = ")
n = int(conn.recvline().strip())
conn.recvuntil(b"you: ")
C_flag = int(conn.recvline().strip())
n2 = n * n
def E_simple(m):
"""无随机性的Paillier加密"""
return pow(n + 1, m, n2)
def homomorphic_add(C1, C2):
"""C_m1 * C_m2 -> m1 + m2"""
return (C1 * C2) % n2
def homomorphic_mul(C, k):
"""C_m^k -> k * m"""
return pow(C, k, n2)
def send_oracle(action, x, y):
conn.recvuntil(b"homomorphism: ")
conn.sendline(action.encode())
conn.recvuntil(b"Parameters: ")
conn.sendline(f"{x},{y}".encode())
response = conn.recvline()
return b"Good job" in response
def get_flag_length():
L_flag = -1
for L in range(10, 70):
print(f"[*] Testing length: {L}")
action = "CTRL-C + CTRL-V"
x = C_flag
# m_y = m_x * (256(L+2) + 256) + 45 * (256(2*L+2) + 256(L+1) + 1)
k1 = pow(256, L + 2) + 256
k2 = 45 * (pow(256, 2 * L + 2) + pow(256, L + 1) + 1)
# C_y = C_flag^k1 * E_simple(k2)
C_k1 = homomorphic_mul(C_flag, k1)
C_k2 = E_simple(k2)
y = homomorphic_add(C_k1, C_k2)
if send_oracle(action, x, y):
L_flag = L
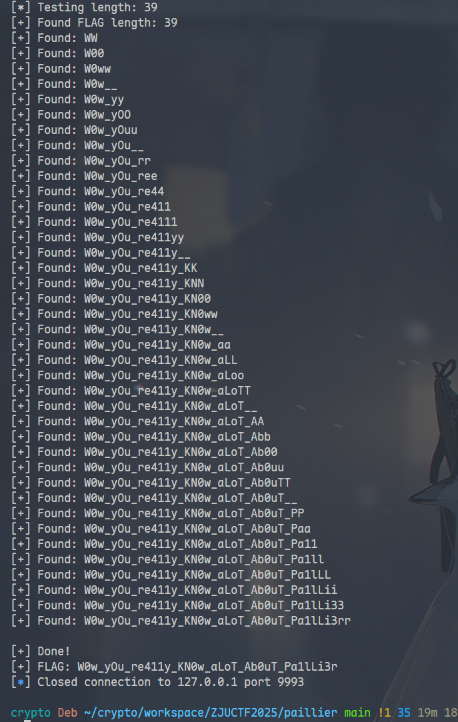
print(f"[+] Found FLAG length: {L_flag}")
break
return L_flag
# L_flag = get_flag_length()
L_flag = 39
known_prefix = b""
for i in range(L_flag):
for g in range(32, 127):
current_char = bytes([g])
guess_prefix = known_prefix + current_char
check_len = L_flag - len(guess_prefix)
m_guess_num = bytes_to_long(guess_prefix) * pow(256, check_len)
C_guess = E_simple(m_guess_num)
C_sub = homomorphic_add(C_flag, pow(C_guess, n - 1, n2))
if check_len == 0:
if send_oracle("STAND STILL ONLY", C_sub, E_simple(0)):
known_prefix += current_char
print(f"\r[+] Found: {known_prefix.decode()}")
break
else:
action = "CTRL-C + CTRL-V"
x = C_sub
k1 = pow(256, check_len + 2) + 256
k2 = 45 * (pow(256, 2 * check_len + 2) + pow(256, check_len + 1) + 1)
C_k1 = homomorphic_mul(x, k1)
C_k2 = E_simple(k2)
y = homomorphic_add(C_k1, C_k2)
if send_oracle(action, x, y):
known_prefix += current_char
print(f"\r[+] Found: {known_prefix.decode()}")
break
print("\n[+] Done!")
print(f"[+] FLAG: {known_prefix.decode()}")
conn.close()
PRNG1/2¶
PRNG1¶
目标服务器实现了一个基于四元数的伪随机数生成器。我们获得前 6 个输出,需要预测全部 20 个输出。四元数乘法是线性的,状态更新规则 \(b_{new} = b_{old} \times a\) 可以看作线性变换。
根据 Cayley-Hamilton 定理,四元数 a 的特征多项式为 \(X^2-2\mathrm{Re}(a)X+|a|^2=0\) ;这意味着序列中的每一项(包括输出的第三分量)都满足二阶线性递推关系:
$$ x_{k+2}\equiv T\cdot x_{k+1}-N\cdot x_k\quad(\mathrm{mod~}p) $$ 其中 \(T=2\mathrm{Re}(a),N=|a|^2\) 。
从递推关系出发,对于任意连续的 5 个输出 \(x_0, x_1, x_2, x_3, x_4\):
同时:
两式相等意味着:
进而有:
我们可以计算多个这样的差值,它们都是 p 的倍数。通过计算这些差值的最大公约数,可以恢复出 p 的倍数。由于 p 是强素数,我们还需要去除结果中的小因子以得到真正的 p,进而得到 T, N。
from pwn import *
import hashlib
import itertools
from Crypto.Util.number import GCD, inverse, isPrime
import string
context.log_level = 'debug'
def PoW(prefix, digest):
import itertools
print(f"Solving PoW: sha256(XXXX + {prefix}) == {digest}")
chars = string.ascii_letters + string.digits
for x in itertools.product(chars, repeat=4):
s = "".join(x)
if sha256((s + prefix).encode()).hexdigest() == digest:
print(f"Found: {s}")
return s
return None
r = remote('127.0.0.1', 11996)
resp = r.recvline().decode().strip()
print(f"PoW Challenge: {resp}")
prefix_part = "sha256(XXXX + "
if prefix_part in resp:
prefix = resp.split(prefix_part)[1].split(')')[0]
digest = resp.split('== ')[1]
else:
print("Unknown PoW format")
return
r.recvuntil(b"Give me XXXX:")
prefix = POW(prefix, digest)
if not prefix:
print("PoW failed")
exit(0)
r.send(prefix.encode())
# Wait for start of BANNER
r.recv(1)
r.sen
known = None
while True:
line = r.recvline().decode().strip()
if not line: continue
if line.startswith('['):
known = eval(line)
break
print(f"Known: {known}")
hint = r.recvline().decode().strip()
print(f"Hint: {hint}")
x = known
diffs = []
# x[k+2] = T * x[k+1] - N * x[k] mod p
# T = (x1*x2 - x0*x3) / (x1^2 - x0*x2)
for i in range(len(x) - 4):
x0, x1, x2, x3, x4 = x[i:i+5]
num1 = x1 * x2 - x0 * x3
den1 = x12 - x0 * x2
num2 = x2 * x3 - x1 * x4
den2 = x22 - x1 * x3
# num1/den1 = num2/den2 mod p
# num1*den2 - num2*den1 = 0 mod p
val = num1 * den2 - num2 * den1
if val != 0:
diffs.append(abs(val))
if not diffs:
print("Could not find p candidates")
exit(0)
p = diffs[0]
for d in diffs[1:]:
p = GCD(p, d)
print(f"Recovered k*p: {p}")
for small in [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31]:
while p % small == 0:
p //= small
print(f"Refined p: {p}")
assert isPrime(p)
# Calculate T and N
x0, x1, x2, x3 = x[0], x[1], x[2], x[3]
try:
den = (x12 - x0 * x2)
inv_den = inverse(den, p)
T = ((x1 * x2 - x0 * x3) * inv_den) % p
N = ((T * x1 - x2) * inverse(x0, p)) % p
print(f"T: {T}")
print(f"N: {N}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error calculating T/N: {e}")
exit(0)
current = list(x)
while len(current) < 20:
next_val = (T * current[-1] - N * current[-2]) % p
current.append(next_val)
print(f"Generated: {current}")
guess_str = "".join(map(str, current))
if hashlib.sha256(guess_str.encode()).hexdigest() == hint:
print("Hash matches!")
else:
print("Hash mismatch!")
for val in current:
r.recvuntil(b"guess: ")
r.sendline(str(val).encode())
r.recvall(timeout=3)
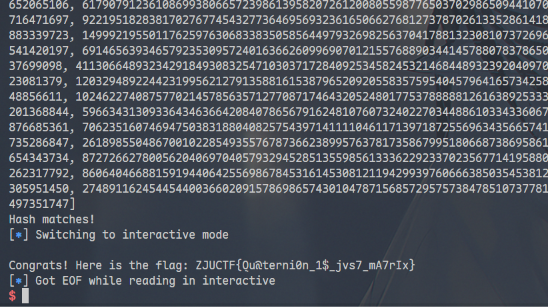
ZJUCTF{ Qu@terni0n_1 $_jvs7_mA7rIx}
PRNG2¶
目标服务器实现了一个基于 CRC(循环冗余校验)的伪随机数生成器。我们获得前 8 个 64-bit 输出,需要预测全部 20 个输出。
next() 函数的核心逻辑可以分解为:
def transform(val):
temp = (1 << 512) - 1
v = val
for _ in range(512):
temp ^= v & 1
temp = (temp >> 1) ^ (self.n & -(temp & 1))
v >>= 1
return temp ^ ((1 << 512) - 1)
这个函数 \(f(x)\) 满足:
- \(f(x \oplus y) = f(x) \oplus f(y)\)
- \(f(c \cdot x) = c \cdot f(x)\)
因此,\(f\) 是 GF(2) 上的线性变换。
因此 CRC 操作在 GF(2) 上是线性的。这意味着状态更新函数可以表示为矩阵乘法:
其中:
- \(S_k\) 是第 \(k\) 步的 512-bit 状态向量(在 GF(2) 上)
- \(M\) 是 \(512 \times 512\) 的转移矩阵
- \(C\) 是 512-bit 的常数向量
构造矩阵 \(M\):
- 计算常数项 \(C = f(0)\)
-
计算基向量的像:对每个基向量 \(e_i = 2^i\) (第 \(i\) 位为 1,其余为 0
) ,计算:
$\(M_i = f(2^i) \oplus C\)$其中 \(M_i\) 是矩阵 \(M\) 的第 \(i\) 列。
-
利用线性性:任意状态 \(x = \sum_{i=0}^{511} x_i \cdot 2^i\) 的像为: $\(f(x) = C \oplus \bigoplus_{i: x_i=1} M_i\)$
def get_matrix_and_constant():
prng = PRNG_PLUS_2(64)
C = prng.transform(0)
M_cols = []
for i in range(512):
val = 1 << i
res = prng.transform(val)
col_val = res ^ C
col_bits = [(col_val >> j) & 1 for j in range(512)]
M_cols.append(col_bits)
M = Matrix(GF(2), M_cols).transpose()
C_vec = vector(GF(2), [(C >> j) & 1 for j in range(512)])
return M, C_vec
定义:
$\(S_k = M \cdot S_{k-1} + C = M^{k-1} \cdot S_1 + \sum_{j=0}^{k-2} M^j \cdot C = M^{k-1} \cdot S_1 + C_{k-1}\)$ 对于第 \(k\) 个输出,我们知道 \(S_k\) 的低 64 位:
对于 \(k = 1, 2, \ldots, 8\):
更准确地说,对于每个 \(k\) 和每个 bit 位置 \(j \in [0, 63]\):
def solve_state(outputs):
M, C = get_matrix_and_constant()
rows = []
rhs = []
current_M = identity_matrix(GF(2), 512)
current_C = vector(GF(2), 512)
for k in range(8):
target_val = outputs[k]
target_bits = [(target_val >> j) & 1 for j in range(64)]
const_bits = [current_C[j] for j in range(64)]
for j in range(64):
rhs.append(target_bits[j] + const_bits[j])
rows.append(current_M[j])
current_C = M * current_C + C
current_M = M * current_M
A_sys = Matrix(GF(2), rows)
B_sys = vector(GF(2), rhs)
print(f"System size: {A_sys.nrows()} x {A_sys.ncols()}")
print(f"System rank: {A_sys.rank()}")
try:
solution = A_sys.solve_right(B_sys)
s1_int = 0
for i in range(512):
if solution[i] == 1:
s1_int |= (1 << i)
kernel = A_sys.right_kernel()
print(f"Kernel dimension: {kernel.dimension()}")
candidates = [s1_int]
if kernel.dimension() > 0:
basis = kernel.basis()
import itertools
for coeffs in itertools.product([0, 1], repeat=kernel.dimension()):
if all(c == 0 for c in coeffs): continue
diff = vector(GF(2), 512)
for i, c in enumerate(coeffs):
if c == 1:
diff += basis[i]
new_sol = solution + diff
cand_int = 0
for i in range(512):
if new_sol[i] == 1:
cand_int |= (1 << i)
candidates.append(cand_int)
return candidates
except ValueError:
print("No solution found")
return []
完整解题代码:
from sage.all import *
from pwn import *
from hashlib import sha256
import string
context.log_level = 'debug'
class PRNG_PLUS_2(object):
"""
copy from prng_plus.py
"""
pass
def get_matrix_and_constant():
prng = PRNG_PLUS_2(64)
C = prng.transform(0)
M_cols = []
for i in range(512):
val = 1 << i
res = prng.transform(val)
col_val = res ^ C
col_bits = [(col_val >> j) & 1 for j in range(512)]
M_cols.append(col_bits)
M = Matrix(GF(2), M_cols).transpose()
C_vec = vector(GF(2), [(C >> j) & 1 for j in range(512)])
return M, C_vec
def solve_state(outputs):
M, C = get_matrix_and_constant()
rows = []
rhs = []
current_M = identity_matrix(GF(2), 512)
current_C = vector(GF(2), 512)
for k in range(8):
target_val = outputs[k]
target_bits = [(target_val >> j) & 1 for j in range(64)]
const_bits = [current_C[j] for j in range(64)]
for j in range(64):
rhs.append(target_bits[j] + const_bits[j])
rows.append(current_M[j])
current_C = M * current_C + C
current_M = M * current_M
A_sys = Matrix(GF(2), rows)
B_sys = vector(GF(2), rhs)
print(f"System size: {A_sys.nrows()} x {A_sys.ncols()}")
print(f"System rank: {A_sys.rank()}")
try:
solution = A_sys.solve_right(B_sys)
s1_int = 0
for i in range(512):
if solution[i] == 1:
s1_int |= (1 << i)
kernel = A_sys.right_kernel()
print(f"Kernel dimension: {kernel.dimension()}")
candidates = [s1_int]
if kernel.dimension() > 0:
basis = kernel.basis()
import itertools
for coeffs in itertools.product([0, 1], repeat=kernel.dimension()):
if all(c == 0 for c in coeffs): continue
diff = vector(GF(2), 512)
for i, c in enumerate(coeffs):
if c == 1:
diff += basis[i]
new_sol = solution + diff
cand_int = 0
for i in range(512):
if new_sol[i] == 1:
cand_int |= (1 << i)
candidates.append(cand_int)
return candidates
except ValueError:
print("No solution found")
return []
def PoW(prefix, digest):
import itertools
print(f"Solving PoW: sha256(XXXX + {prefix}) == {digest}")
chars = string.ascii_letters + string.digits
for x in itertools.product(chars, repeat=4):
s = "".join(x)
if sha256((s + prefix).encode()).hexdigest() == digest:
print(f"Found: {s}")
return s
return None
r = remote('127.0.0.1', 4078)
line = r.recvline().decode().strip()
if "sha256" in line:
parts = line.split()
suffix = parts[2][:-1]
digest = parts[4]
ans = PoW(suffix, digest)
r.sendlineafter(b"Give me XXXX:", ans.encode())
r.recvuntil(b"Level: ")
r.sendline(b"2")
line = r.recvline().decode().strip()
if not line:
line = r.recvline().decode().strip()
known = eval(line)
print(f"Known outputs: {known}")
# Receive hint
hint = r.recvline().decode().strip()
print(f"Hint: {hint}")
# Solve
print("Solving for state...")
candidates = solve_state(known)
print(f"Found {len(candidates)} candidates")
correct_outputs = None
for s1_cand in candidates:
prng_rec = PRNG_PLUS_2(64)
prng_rec.a = s1_cand
rec_outputs = [known[0]]
for _ in range(19):
rec_outputs.append(prng_rec.next())
# Check hint
rec_hint = sha256("".join(map(str, rec_outputs)).encode()).hexdigest()
if rec_hint == hint:
print("Found correct state!")
correct_outputs = rec_outputs
break
if correct_outputs:
for i in range(20):
r.recvuntil(b"guess: ")
r.sendline(str(correct_outputs[i]).encode())
r.interactive()
else:
print("Failed to recover state matching hint.")
r.close()
(忘记截图了)
ZJUCTF{ U_@irEad1_kn0w_CRC_1s_lIneaR }
easy_poly¶
- 需要恢复 32 个系数,每个系数约 32 bits,总共约 1024 bits 的信息
- 每次查询只能得到 \(f(x) \pmod m\) ,且 m 不可重复
sage: total_info_bit = 0
sage: for p in primes(750):
....: total_info_bit += p.bit_length()
sage: total_info_bit
1097
理论上我们可以获得 1097 bits 的信息,可行,尝试 LLL;格能够找到解,但是会时间过长,服务器只给我们 10 s。
尝试降维:
- 恢复 \(a_0\)
- 使用最小的若干个素数,查询点 \(x=0\)
- 此时 \(f(0) = a_0\)
- 通过 CRT 恢复 \(a_0\)
- 对于 \(a_{31}\),我们猜测其高 \(k\) 位:
- \(a_{31} = (\text{guess} \ll (32-k)) + a_{31\_\text{low}}\)
- 在权衡猜测次数和 LLL 求解用时的乘积后,选择 k=4
调整后的方程:
对于 31 个未知数(\(a_1, \ldots, a_{30}, a_{31\_\text{low}}\)
其中:
- \(W = 2^{100}\),约束最后一列为 0
- \(C_i\):CRT 预计算的常数
- \(M = \prod m_j\):模数乘积
- \(Y'\):调整后的目标值(将 \(a_i \in [0, p)\) 映射到 \([-p/2, p/2)\),减小目标向量的范数)
from sage.all import *
from pwn import *
import time
context.log_level = 'debug'
primes_list = list(primes(750))
io = remote('127.0.0.1', 12719)
# Get p
io.recvuntil(b"p = ")
p_val = int(io.recvline().strip())
log.info(f"p = {p_val}")
# Recover a0
p_prod = 1
primes_for_a0 = []
idx = 0
while p_prod <= p_val and idx < len(primes_list):
m = primes_list[idx]
p_prod *= m
primes_for_a0.append(m)
idx += 1
remaining_primes = primes_list[idx:]
log.info(f"Using {len(primes_for_a0)} primes for a0 recovery.")
payload = ""
# Queries for a0 (x=0)
for m in primes_for_a0:
payload += f"1\n{m}\n0\n"
# Queries for lattice (random x)
lattice_queries = []
for m in remaining_primes:
x = randint(0, m-1)
lattice_queries.append((m, x))
payload += f"1\n{m}\n{x}\n"
log.info(f"Sending {len(primes_for_a0) + len(lattice_queries)} queries...")
io.send(payload)
# For a0
a0_residues = []
for _ in primes_for_a0:
io.recvuntil(b"result = ")
res = int(io.recvline().strip())
a0_residues.append(res)
a0_recovered = CRT_list(a0_residues, primes_for_a0)
log.info(f"Recovered a0: {a0_recovered}")
# For lattice
results = []
moduli = []
x_vals = []
for m, x in lattice_queries:
io.recvuntil(b"result = ")
res = int(io.recvline().strip())
results.append(res)
moduli.append(m)
x_vals.append(x)
log.info("Received all results.")
# We want a1...a31
# sum_{i=1}^{31} a_i x^i = Y - a_0
C = []
for k in range(1, 32):
residues = [pow(int(x_val), int(k), int(m)) for m, x_val in zip(moduli, x_vals)]
c_val = CRT_list(residues, moduli)
C.append(c_val)
M = prod(moduli)
log.info(f"Modulus size: {M.nbits()} bits")
Y_raw = CRT_list(results, moduli)
Y = (Y_raw - a0_recovered) % M
# Guess top bits of a31
bits_to_guess = 4
guess_limit = 1 << bits_to_guess
shift_amount = 32 - bits_to_guess
# Centering shifts
# a1..a30: p//2
# a31_low: (1<<shift_amount)//2
shifts = [p_val // 2] * 30 + [(1 << shift_amount) // 2]
# Base Matrix
dim = 33 # 30 vars (a1..a30) + 1 var (a31_low) + 1 modulus + 1 embedding
W = 2100
mat = Matrix(ZZ, dim, dim)
# a1..a30
for i in range(30):
mat[i, i] = 1
mat[i, 32] = W * C[i]
# a31_low
mat[30, 30] = 1
mat[30, 32] = W * C[30] # C[30] corresponds to x^31
mat[31, 32] = W * M
mat[32, 31] = 1
log.info(f"Iterating {guess_limit} guesses...")
for guess in range(guess_limit):
# Adjust Y for guess
# a31 = guess << shift + low
# term = (guess << shift) * x^31 + low * x^31
# We move known part to RHS
term_known = (guess << shift_amount) * C[30] # C[30] is x^31
Y_adjusted = (Y - term_known) % M
# Centering correction
shift_correction = sum(s * c for s, c in zip(shifts, C))
Y_prime = (Y_adjusted - shift_correction) % M
mat[32, 32] = -W * Y_prime
L = mat.LLL()
# L = mat.BKZ(block_size=20)
for row in L:
if row[32] == 0 and abs(row[31]) == 1:
sign = 1 if row[31] == 1 else -1
coeffs_found_partial = []
for i in range(30):
coeffs_found_partial.append(sign * row[i] + shifts[i])
a31_low = sign * row[30] + shifts[30]
a31_found = (guess << shift_amount) + a31_low
coeffs_found = [a0_recovered] + coeffs_found_partial + [a31_found]
if all(0 <= c < p_val for c in coeffs_found):
log.info(f"Found candidate with guess {guess}")
# Send answer
payload_ans = "2\n" + " ".join(str(c) for c in coeffs_found) + "\n"
io.send(payload_ans)
# Check response
try:
resp = io.recvline(timeout=1)
if b"Correct" in resp:
log.success(f"Flag: {resp}")
print(resp.decode())
io.interactive()
exit(0)
else:
log.warning("Wrong answer")
except:
pass
print("Failed to find coefficients")
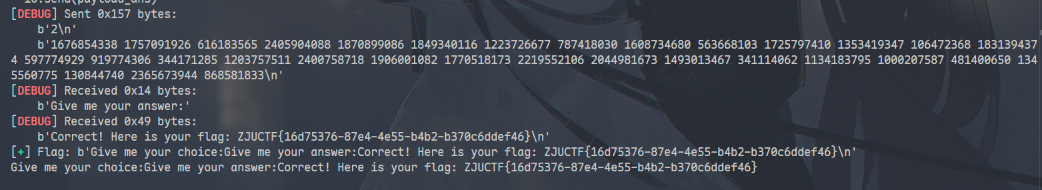
ZJUCTF{16d75376-87e4-4e55-b4b2-b370c6ddef46}
curve2¶
给定一个在 \(\mathbb{F}_p\) 上的超椭圆曲线(\(p\) 随机
- 题目没有给出 \(f(x)\),但给出了 Jacobian 群上的点 \(D\) 和 \(D_2\)。在 Mumford 表示法中,点 \(D\) 由多项式对 \((u, v)\) 表示,满足 \(f(x) \equiv v(x)^2 \pmod{u(x)}\)。我们可以收集几轮的 \(D_2\) 点,利用多项式中国剩余定理(CRT)恢复出 \(f(x)\)
- 恢复 \(f(x)\) 后,利用 SageMath 的
HyperellipticCurve(f).jacobian().polynomial()可以计算出 Jacobian 群的阶 \(N\) - 由于 \(k\) 是 16 位素数(小于 65536
) ,我们可以预先计算所有可能的 \(k \cdot D\) 并存入哈希表,空间换时间 - 对于每一轮,通过查表找到 \(k\),然后计算 \(k_2 = k^{-1} \pmod{N}\) 并发送。
from pwn import remote
from sage.all import *
import re
def parse_jacobian_point(s, R):
s = s.strip('()')
u_str, v_str = s.split(', ')
u = R(u_str)
v = R(0)
if 'y' in v_str:
v_part = v_str.replace('y', '').strip()
if v_part:
v = -R(v_part)
return u, v
io = remote('127.0.0.1', 12421)
io.recvuntil(b'p=')
p = int(io.recvline().strip())
R = PolynomialRing(GF(p), 'x')
io.recvuntil(b'D=')
D_str = io.recvline().strip().decode()
u_D, v_D = parse_jacobian_point(D_str, R)
io.recvuntil(b'D2=')
D2_str1 = io.recvline().strip().decode()
io.sendlineafter(b'k2=', b'1')
io.recvuntil(b'D2=')
D2_str2 = io.recvline().strip().decode()
u_D2_1, v_D2_1 = parse_jacobian_point(D2_str1, R)
u_D2_2, v_D2_2 = parse_jacobian_point(D2_str2, R)
us = [u_D, u_D2_1, u_D2_2]
vs = [v_D, v_D2_1, v_D2_2]
f = CRT([v2 for v in vs], us)
H = HyperellipticCurve(f)
J = H.jacobian()(GF(p))
D = J([u_D, v_D])
primes = [i for i in range(215, 216) if is_prime(i)]
table = {str(k * D): k for k in primes}
for _ in range(19):
io.recvuntil(b'D2=')
D2_str = io.recvline().strip().decode()
u_D2, v_D2 = parse_jacobian_point(D2_str, R)
D2 = J([u_D2, v_D2])
k = table.get(str(D2))
if k is None:
io.sendlineafter(b'k2=', b'1')
else:
order = H.frobenius_polynomial()(1)
k2 = inverse_mod(k, order)
io.sendlineafter(b'k2=', str(k2).encode())
io.recvall(timeout=3)
ZJUCTF{Getting$Started?In^Hyperelliptic-Curve}